Be Golden as gold mine & Green as leaf
carpe diemBe Golden as gold mine & Green as leaf
carpe diemFun Diery
There's funny and odd song which i like to sing but my friend Sarvi doesn't like it cause it knot your tongue

!!!!!!!
So I decided to post it for U too have fun and try to say it correct:
Three witches ,watch three switch watches ,which which watch witch switch watch!!!!

Heeeeeeeeee
That's why sarvi didn't like it

Every Thing about Brain
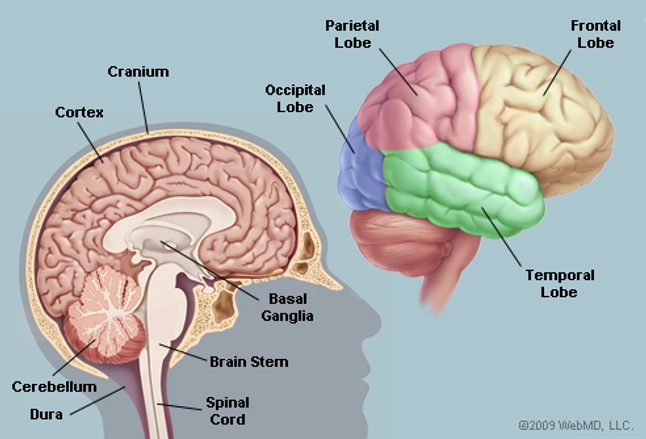
The brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the human body.
It is made up of more than 100 billion nerves that communicate in trillions of connections called synapses.
The brain is made up of many specialized areas that work together:
• The cortex is the outermost layer of brain cells. Thinking and voluntary movements begin in the cortex.
• The brain stem is between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. Basic functions like breathing and sleep are controlled here.
• The basal ganglia are a cluster of structures in the center of the brain. The basal ganglia coordinate messages between multiple other brain areas.
• The cerebellum is at the base and the back of the brain. The cerebellum is responsible for coordination and balance.
The brain is also divided into several lobes:
• The frontal lobes are responsible for problem solving and judgment and motor function.
• The parietal lobes manage sensation, handwriting, and body position.
• The temporal lobes are involved with memory and hearing.
• The occipital lobes contain the brain's visual processing system.
The brain is surrounded by a layer of tissue called the meninges. The skull (cranium) helps protect the brain from injury.
ADVERTISEMENT
Brain Conditions
Headache: There are many types of headaches; some can be serious but most are not and are generally treated with analgesics/painkillers.
Stroke (brain infarction): Blood flow and oxygen are suddenly interrupted to an area of brain tissue, which then dies. A blood clot, or bleeding in the brain, are the cause of most strokes.
Brain aneurysm: An artery in the brain develops a weak area that swells, balloon-like. A brain aneurysm rupture can causes a stroke.
Subdural hematoma: Bleeding within or under the dura, the lining inside of the skull. A subdural hematoma may exert pressure on the brain, causing neurological problems.
Epidural hematoma: Bleeding between the tough tissue (dura) lining the inside of the skull and the skull itself, usually shortly after a head injury. Initial mild symptoms can progress rapidly to unconsciousness and death, if untreated.
Intracerebral hemorrhage: Any bleeding inside the brain.
Concussion: A brain injury that causes a temporary disturbance in brain function. Traumatic head injuries cause most concussions.
Cerebral edema: Swelling of the brain tissue in response to injury or electrolyte imbalances.
Brain tumor: Any abnormal tissue growth inside the brain. Whether malignant (cancer) or benign, brain tumors usually cause problems by the pressure they exert on the normal brain.
Glioblastoma: An aggressive, malignant brain tumor (cancer). Brain glioblastomas progress rapidly and are very difficult to cure.
Hydrocephalus: An abnormally increased amount of cerebrospinal (brain) fluid inside the skull. Usually this is because the fluid is not circulating properly.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus: A form of hydrocephalus that often causes problems walking, along with dementia and urinary incontinence. Pressures inside the brain remain normal, despite the increased fluid.
Meningitis: Inflammation of the lining around the brain or spinal cord, usually from infection. Stiff neck, neck pain, headache, fever, and sleepiness are common symptoms.
Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain tissue, usually from infection with a virus. Fever, headache, and confusion are common symptoms.
Traumatic brain injury: Permanent brain damage from a traumatic head injury. Obvious mental impairment, or more subtle personality and mood changes can occur.
Parkinson's disease: Nerves in a central area of the brain degenerate slowly, causing problems with movement and coordination. A tremor of the hands is a common early sign.
Huntington's disease: An inherited nerve disorder that affects the brain. Dementia and difficulty controlling movements (chorea) are its symptoms.
Epilepsy: The tendency to have seizures. Head injuries and strokes may cause epilepsy, but usually no cause is identified.
Dementia: A decline in cognitive function resulting from death or malfunction of nerve cells in the brain. Conditions in which nerves in the brain degenerate, as well as alcohol abuse and strokes, can cause dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease: For unclear reasons, nerves in certain brain areas degenerate, causing progressive dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia.
Brain abscess: A pocket of infection in the brain, usually by bacteria. Antibiotics and surgical drainage of the area are often necessary.
Those who want to be Neurologist come on !!!
Is Neurology a Good Career Choice? Here’s Everything You Need to Know!
In this day and age, it is difficult to find a career you really want to commit to. With people changing careers several times over their lives, it is hard to know what you want to do and what steps you need to take to get there. An interesting career that people often shy away from because of its intimidating name is neurology. Neurologists are using medical advancements – while at the same time advancing medicine – to change lives and improve how we understand the neurological system. For someone who is interested in these objectives and is skilled in the field of science, becoming a neurologist can be a very rewarding career choice. It is also worth mentioning that a neurologist salary is also very rewarding! Even on those days when work is overwhelming and the world seems to be working against you, a neurologist can take pride in the fact that their work is positively impacting humanity.
What Is Neurology?
Simply put, neurology is the study of the human nervous system. The nervous system refers to the brain, spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous network, which are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. Neurology also studies the autonomic nervous system, which is the system that functions as the control center for heart rate and digestion. Neurology studies deviations in these systems. The field of neurology includes research on neurological disorders and, when possible, how to remedy these disorders.
What Does a Neurologist Do?
A neurologist is a trained physician who has chosen to focus specifically on neurological disorders. They have been specifically taught how to identify these disorders and how to treat them. At times, a neurologist’s job can focus heavily on patient care, while at other times their career can be more research-driven. Of course, research and patient care do go hand in hand, and many neurologists combine the two by running clinical trials or by doing clinical research.
However, the specific thing that differentiates neurologists from other scientists who study the brain – such as neuroscientists – is that neurology specifically focuses on the disorders of the nervous system and not the nervous system in its totality. For example, a neurologist does not perform surgery. However they may work with a neurosurgeon to determine the best course of treatment for a patient.
The Process of Becoming a Neurologist
When people hear about how rewarding becoming a neurologist can be, in combination with the monetary rewards of a neurologist salary, the natural question on their minds is how to become a neurologist. The fact that becoming a neurologist requires a lot of hard work and intense schooling is obvious; it is not a career for the faint hearted. Becoming a neurologist takes an incredible amount of discipline and focus, as well as dedication and sacrifice.
Because each country has a slightly different post-secondary education structure, it is almost impossible to detail the requirements for breaking into neurology in every country. However, usually the study of neurology is a specialty that people enter into after completing their medical school education. Depending on how specialized a person wants to become in the field of neurology, their education can last between 10 and 13 years. After obtaining a general neurology specialty, they can then choose to learn more about other aspects of neurology such as epilepsy, neurodevelopment disabilities or neuro-rehabilitation. The field has a lot of depth and it is possible for neurologists to become extremely specialized and highly trained individuals if they so choose.
A Neurologist’s Typical Work Day
A neurologist will experience a varied workday and a stimulating work environment. An average day for a neurologist can consist of seeing patients in their office where they will examine them, and can also include a visit to the hospital where they will meet with newly admitted patients to review their symptoms and track their progress. Like any medical professional, neurologists are expected to put in long hours and work hard; there are often many patients to see each day. Because of the nature of health care, neurologists are also often required to be “on call” and ready to visit a patient if an emergency occurs. A neurologist’s schedule is structured around the needs of their patients.
Is Neurology A Good Career Choice For You?
Neurology is obviously a career that requires lots of quality work to even enter into; it requires many years of schooling and a love for science and medicine. If you consider yourself to be less of an academic, then neurology is probably not a great choice for you. If, however, you are not intimidated by the idea of putting in several years of post secondary education, neurology might be a great field to invest your time in.
Neurologists have the chance to see incredible medical breakthroughs and truly make a positive impact in the lives of their patients. For many people, a good neurologist can give them hope that their suffering might be eliminated. Though neurology is a very demanding career, it is also a career that comes with a high level of satisfaction. As a neurologist, you know that you are making a positive impact in the lives of many. In the end, the choice is up to you. You must weigh the reward of beginning a career in neurology with the cost of the education required
Guys I love to study Neurology in university and I love to know more about it so I posted these informations for U
 I wish U enjoy it as much as I do..
I wish U enjoy it as much as I do..